Sunday, November 8, 2009
Revit 2010: View Control Bar

Revit 2010: Type Selector
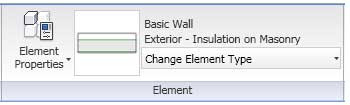 To change existing elements to a different type, select one or more elements of the same category. Then use the Type Selector to select the desired type.
To change existing elements to a different type, select one or more elements of the same category. Then use the Type Selector to select the desired type.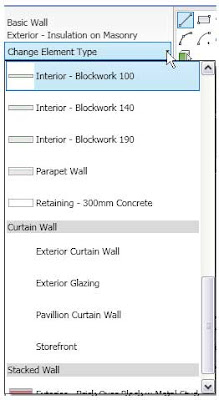
Revit 2010: Options Bar
Revit 2010: Status Bar (Hints About What to Do Next)
"If you start a command (such as Rotate) and are not sure what to do next, check the status bar. It often displays tips or hints about what to do next for the current command. In addition, a tool tip appears next to the cursor, displaying the same information.
To cancel or exit the current command, do either of the following:
- Press Esc twice.
- On the Quick Access toolbar, click Modify."
Revit 2010: Using the Quick Access Toolbar
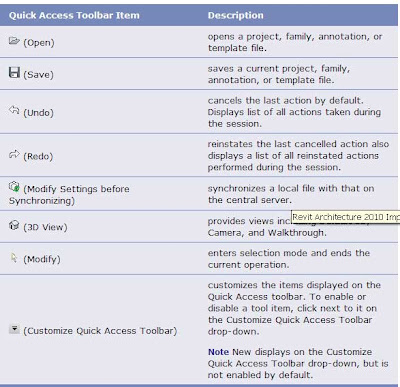
To undo or redo a series of operations, click the drop-down to the right of the Undo and Redo buttons. This displays the command history in a list. Starting with the most recent command, you can select any number of previous commands to include in the Undo or Redo operation.
The Quick Access toolbar can display below the ribbon. Click Show Below the Ribbon on the Customize Quick Access Toolbar to change the display setting.
While in an edit mode (such as Place a Wall), or the Family Editor, items that are added to the Quick Access toolbar from the Create, Modify, Group, Clipboard, or View Graphics panel persist on the toolbar for that mode. However, when you switch to another editing mode, these items do not display and need to be re-added to the Quick Access toolbar.
Saturday, November 7, 2009
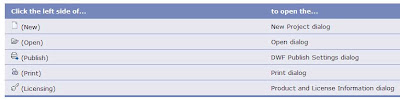
Revit 2010: Access Common Tools
Access common tools to start or publish a file in the application menu.
Click  to quickly perform the following actions:
to quickly perform the following actions:
- Create a file
- Open an existing file
- Save a file
- Export a file to another file format
- Publish a file and place it in a central or shared location
- Print a file
- Access license information
- Close the application
You can quickly access the following dialogs from the application menu:
Revit 2010: The Application Menu
Revit 2010: Application Frame Overview
"The application frame contains tools and provides feedback to help you manage your Revit Architecture projects.
The application frame consists of five main areas described in the following table:
 "
"
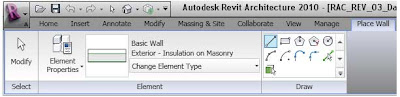
Revit 2010: Contextual Ribbon Tabs
For example, when drawing walls, the Place Wall contextual tab displays that has 3 panels:
- Select: contains the Modify command.
- Element: contains Element Properties and the Type Selector.
- Draw: contains the draw editors necessary for creating the wall.
This contextual ribbon tab closes once you end the command.
 "
"
Revit 2010: Ribbon - Expanded Panels
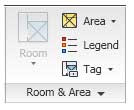
Revit 2010: Ribbon Tabs and Panels
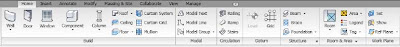
The following table describes the ribbon tabs and the types of commands they contain.
Revit 2010: Ribbon Overview
Revit 2010: Understanding Terms
"Most of the terms used to identify objects in Revit Architecture are common, industry-standard terms familiar to most architects. However, some terms are unique to Revit Architecture. Understanding the following terms is crucial to understanding the software.
Project: In Revit Architecture, the project is the single database of information for your design—the building information model. The project file contains all information for the building design, from geometry to construction data. This information includes components used to design the model, views of the project, and drawings of the design. By using a single project file, Revit Architecture makes it easy for you to alter the design and have changes reflected in all associated areas (plan views, elevation views, section views, schedules, and so forth). Having only one file to track also makes it easier to manage the project.
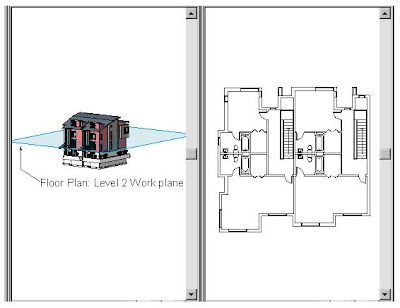
Level: Levels are infinite horizontal planes that act as a reference for level-hosted elements, such as roofs, floors, and ceilings. Most often, you use levels to define a vertical height or story within a building. You create a level for each known story or other needed reference of the building; for example, first floor, top of wall, or bottom of foundation. To place levels, you must be in a section or elevation view.
Level 2 work plane cutting through the 3D view with the corresponding floor plan next to it
 Element: When creating a project, you add Revit Architecture parametric building elements to the design. Revit Architecture classifies elements by categories, families, and types.
Element: When creating a project, you add Revit Architecture parametric building elements to the design. Revit Architecture classifies elements by categories, families, and types.Category: A category is a group of elements that you use to model or document a building design. For example, categories of model elements include walls and beams. Categories of annotation elements include tags and text notes.
Family: Families are classes of elements in a category. A family groups elements with a common set of parameters (properties), identical use, and similar graphical representation. Different elements in a family may have different values for some or all properties, but the set of properties—their names and meaning—is the same. For example, 6-panel colonial doors could be considered one family, although the doors that compose the family come in different sizes and materials.
There are 3 kinds of families:
- Loadable families can be loaded into a project and created from family templates. You can determine the set of properties and the graphical representation of the family.
- System families include walls, dimensions, ceilings, roofs, floors, and levels. They are not available for loading or creating as separate files.
- Revit Architecture predefines the set of properties and the graphical representation of system families.
- You can use the predefined types to generate new types that belong to this family within the project. For example, the behavior of a wall is predefined in the system. However, you can create different types of walls with different compositions.
- System families can be transferred between projects.
- In-place families are custom families that you create in the context of a project. Create an in-place family when your project needs unique geometry that you do not expect to reuse or geometry that must maintain one of more relationships to other project geometry.
- Because in-place families are intended for limited use in a project, each in-place family contains only a single type. You can create multiple in-place families in your projects, and you can place copies of the same in-place family element in your projects. Unlike system and standard component families, you cannot duplicate in-place family types to create multiple types.
Type: Each family can have several types. A type can be a specific size of a family, such as a 30” X 42” title block or a 32" x 84" door. A type can also be a style, such as default aligned or default angular style for dimensions.
Instance: Instances are the actual items (individual elements) that are placed in the project and have specific locations in the building (model instances) or on a drawing sheet (annotation instances).
Revit 2010: Element behavior in a parametric modeler
"In projects, Revit Architecture uses 3 types of elements:
- Model elements represent the actual 3D geometry of the building. They display in relevant views of the model. For example, walls, windows, doors, and roofs are model elements.
- Datum elements help to define project context. For example, grids, levels, and reference planes are datum elements.
- View-specific elements display only in the views in which they are placed. They help to describe or document the model. For example, dimensions, tags, and 2D detail components are view-specific elements.
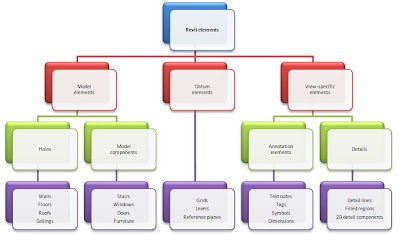
There are 2 types of model elements:
- Hosts (or host elements) are generally built in place at the construction site. For example, walls and roofs are hosts.
- Model components are all the other types of elements in the building model. For example, windows, doors, and cabinets are model components.
There are 2 types of view-specific elements:
- Annotation elements are 2D components that document the model and maintain scale on paper. For example, dimensions, tags, and keynotes are annotation elements.
- Details are 2D items that provide details about the building model in a particular view. Examples include detail lines, filled regions, and 2D detail components.
This implementation provides flexibility for designers. Revit Architecture elements are designed to be created and modified by you directly; programming is not required. If you can draw, you can define new parametric elements in Revit Architecture.
In Revit Architecture, the elements determine their behavior largely from their context in the building. The context is determined by how you draw the component and the constraint relationships that are established with other components. Often, you do nothing to establish these relationships; they are implied by what you do and how you draw. In other cases, you can explicitly control them, by locking a dimension or aligning 2 walls, for example."
Revit 2010: How does it keep things updated?
Revit Architecture uses 2 key concepts that make it especially powerful and easy to use. The first is the capturing of relationships while the designer works. The second is its approach to propagating building changes. The result of these concepts is software that works like you do, without requiring entry of data that is unimportant to your design."
Revit 2010: What is meant by parametric?
The following are examples of these element relationships:
- The outside of a door frame is a fixed dimension on the hinge side from a perpendicular partition. If you move the partition, the door retains this relationship to the partition.
- Windows or pilasters are spaced equally across a given elevation. If the length of the elevation is changed, the relationship of equal spacing is maintained. In this case, the parameter is not a number but a proportional characteristic.
- The edge of a floor or roof is related to the exterior wall such that when the exterior wall is moved, the floor or roof remains connected. In this case, the parameter is one of association or connection."
What is Autodesk Revit Architecture 2010?
In the Revit Architecture model, every drawing sheet, 2D and 3D view, and schedule is a presentation of information from the same underlying building model database. As you work in drawing and schedule views, Revit Architecture collects information about the building project and coordinates this information across all other representations of the project. The Revit Architecture parametric change engine automatically coordinates changes made anywhere—in model views, drawing sheets, schedules, sections, and plans."